Editor in Chief of Constellation Insights
Constellation Research
About Larry Dignan:
Dignan was most recently Celonis Media’s Editor-in-Chief, where he sat at the intersection of media and marketing. He is the former Editor-in-Chief of ZDNet and has covered the technology industry and transformation trends for more than two decades, publishing articles in CNET, Knowledge@Wharton, Wall Street Week, Interactive Week, The New York Times, and Financial Planning.
He is also an Adjunct Professor at Temple University and a member of the Advisory Board for The Fox Business School's Institute of Business and Information Technology.
Constellation Insights does the following:
Cover the buy side and sell side of enterprise tech with news, analysis, profiles, interviews, and event coverage of vendors, as well as Constellation Research's community and…...
Read more
Amazon Web Services made the case at re:Invent that it should be your complete AI stack with Amazon Q, a horizontal generative AI tool that will be embedded throughout AWS and backed up with Amazon Bedrock and infrastructure for model training and inference powered by Trainium and Inferentia processors.
The catch? AWS' strategy rhymes with Microsoft's copilot everywhere plans as well as Google Cloud's Duet AI plans. The interesting twist for AWS is that it's more horizontal across the platform instead of focused on one application, use case or role. AWS also had a big developer spin on Amazon Q, which is seen as an ally to developers because it can connect code and infrastructure.
For enterprises, the big question is whether they will go with one AI stack or multiple. And is that decision made by CXOs or developers? Time will tell, but for now the biggest takeaway from re:Invent is that AWS is taking its entire portfolio generative AI with a bevy of additions that are in preview.
Adam Selipsky, CEO of AWS, said during his re:Invent keynote AWS has been leveraging AI for decades and now plans to reinvent generative AI. "We're ready to help you reinvent with generative AI," said Selipsky, who said experimentation is turning into real world productivity gains.

Selipsky said AWS is investing in all layers of the generative AI stack. "It's still early days and customers are finding different models work better than others," said Selipsky. "Things are moving so fast that the ability to adapt is best capability you can have. There will be multiple models and switch between them and combine them. You need a real choice."
In a veiled reference to OpenAI, Selipsky said "the events of the last few days illustrate why model choice matters."
Here's a look at the moving parts of AWS' generative AI strategy as outlined by Selipsky and other executives.
Top layer of AWS' AI stack is Q
Amazon Q is billed as "a new type of generative AI assistant that's an expert in your business."
AWS' answer to Microsoft's Azure's copilot everywhere theme is Amazon Q. According to AWS, Q will engage in conversation to solve problems, generate content and then take action. It'll know your code, personalize interactions by role and permissions and be built to be private.
The vision for Amazon Q is to do everything from answering software development questions to be a resource for HR to monitor and enhance customer experiences. The most interesting theme is that AWS is playing to its strengths--code and infrastructure--and using Q to connect the dots.

"AWS had built a bevy of cross services capabilities and Amazon Q is the next evolution," said Constellation Research analyst Holger Mueller.
Mueller said:
"What sets Q apart is that it has a shot to provide one single assistant across all of AWS services. Q reduces one of the main challenges of AWS--the complexity introduced by the thousands of services offered. But it is only possible because Amazon has been working on the integration layer across its services, starting from access and security over an insights layer, one foundation with SageMaker for all AI and e.g. Data Zone. It can now collect the benefit and has a shot at redefining the future of work. Partnerships with SAP, Salesforce, Workday and more ERP vendors make it easily the Switzerland of GenAI assisted work in the multi-vendor enterprise.â€
Doug Henschen, Constellation Research analyst, crystallized the significance of Amazon Q. He said:
"Amazon Q was the most broadly compelling and exciting GenAI announcement during Adam Selipsky’s keynote. Amazon Q is an AI assistant that will engage in conversations based on understanding of company-specific information, code, and technology systems. The promise is personalized interactions based on user-specific roles and permissions. AWS previously offered QuickSight Q for natural language querying within its QuickSight analytics platform, but Amazon Q is single, all-purpose GenAI assistant. The idea is to deliver a AI assistant that will understand the context of data, text, and code. At this point they have some 40 connectors to popular enterprise systems outside of AWS, such as Office 365, Google cloud apps, Dropbox and more. The promise is nuanced, contextual understanding of what users are seeking when they ask questions in natural language."
Here's how Amazon Q will be leveraged:
- Developers and builders will use Amazon Q to architect, troubleshoot and optimize code, develop features and transform code based on 17 years of AWS knowledge.
- For lines of business Amazon Q is about getting answers to questions with access controls and complete actions.
- Specialists will get Amazon Q in QuickSight, Connect and Supply Chain.
Selipsky said AI chat applications are falling short because they're in silos by use cases and applications. "They don't know your business or how you operate securely," said Selipsky. "Amazon Q is designed to work for you at work. We've designed Q to meet your stringent enterprise requirements from day one."

What's interesting for enterprise buyers is the approach of Amazon Q. Does a horizontal approach to generative AI across multiple functions curb model sprawl?
Amazon Bedrock: More choices, more relevancy after OpenAI fiasco?
Amazon added new models to Bedrock, added secure customization and fine tuning of models, agents to complete tasks, automated model evaluation tools as well as knowledge bases.
Specifically, new models added to Bedrock include:
- Claude 2.1;
- Llama 2 Chat with 13 billion and 70 billion parameters;
- Stable Diffusion XL;
- Titan models focused on generating images and multimodel embeddings;
- Command Light & Embed.
- Fine tuning will be available for Meta Llama 2, Cohere Command and Titan with Claude 2 coming soon.
Selipsky said enterprises need to orchestrate between models and get foundational models to take actions.

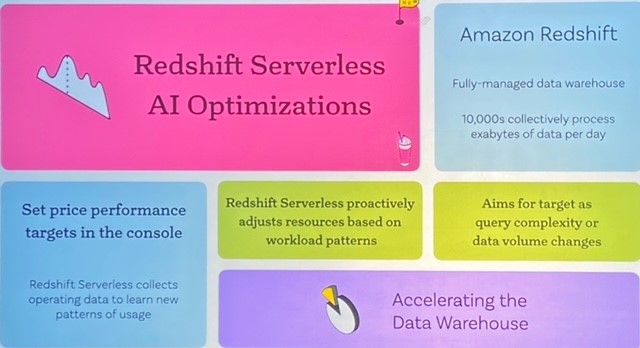
To support this level, AWS has integrated AI capabilities into its data services such as Redshift and Aurora. Redshift Serverless will get a bevy of AI optimizations. AI will also be used to simplify application management on AWS.
The breakdown of the data pieces underpinning the broader AI strategy for AWS include:
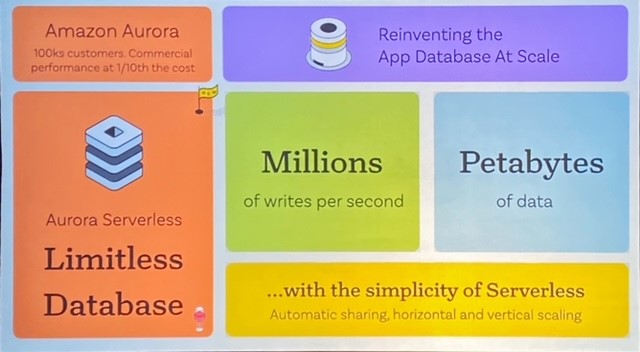
- Amazon Aurora Limitless Database, which supports automated horizontal scaling of write capacity. Constellation Research analyst Doug Henschen noted "Aurora Limitless Database is an important step forward in potentially matching rivals such as Oracle on automated scalability."
- Redshift Serverless AI Optimizations, which brings machine learning scaling and optimization to AWS analytical database for data warehousing. Henschen said "matching rivals by adding sophisticated, ML-based scaling and optimization capabilities with cost guardrails will make Redshift more efficient and performant as well as even more cost competitive."
- AWS Introduces Two Important Database Upgrades at Re:Invent 2023
Trainium, Inferentia with a dash of SageMaker
AWS launched the latest versions of its Trainium and Inferentia processors, two GPUs that may be able to bring the price of model training down. Today, AI workloads are dominated by Nvidia and AMD is entering the market.
However, AWS has had GPUs in the market and has been able to acquire workloads for enterprises that may not need Nvidia's horsepower. Here's the breakdown:
- For training generative AI models, AWS launched Trainium2, which is 4x faster than its previous version and operates at 65 exaflops.
- For using generative AI models and inference, AWS launched Inferentia2, which has 4x the throughput of the previous version and 10x lower latency.
- Riding on top of these processors is SageMaker HyperPod, which can reduce the time to train foundation models by up to 40%. AWS said SageMaker HyperPod can distribute model training in parallel with 1000s of accelerators, automatic checkpointing and resiliency.
AWS also added Inference Optimization to SageMaker and said the new service can reduce foundation model deployment cost by an average of 50% with intelligent routing, scaling policies and better efficiency by deploying multiple models to the same instance.
Bottom line: AWS made its case to be the generative AI stack for enterprises, but Henschen noted there were a lot of things in preview. One thing is clear: Selipsky's not-so-veiled references to Microsoft Azure and OpenAI illustrate that the narrative gloves are coming off.

Data to Decisions
Innovation & Product-led Growth
Future of Work
Tech Optimization
Next-Generation Customer Experience
Digital Safety, Privacy & Cybersecurity
amazon
AI
GenerativeAI
ML
Machine Learning
LLMs
Agentic AI
Analytics
Automation
Disruptive Technology
Chief Information Officer
Chief Executive Officer
Chief Technology Officer
Chief AI Officer
Chief Data Officer
Chief Analytics Officer
Chief Information Security Officer
Chief Product Officer