C3.ai's next move: Convert generative AI pilots to production deals
C3.ai's fiscal second quarter results showed promise, but the biggest challenge facing the company is abundantly clear: It has to convert pilots to production to start collecting consumption revenue at scale.
If pilots with customers (prospective or existing) were revenue, C3.ai would be putting up stronger sales gains. Part of the issue with C3.ai's second quarter is expectations. If the company is going to live up to its billing as an enterprise generative AI juggernaut it should have stronger growth.
Another wrinkle is that C3.ai transitioned its revenue model to one based on consumption-based pricing from licensing. That transition equates to more predictable revenue in the future, but there is a transition. C3.ai used to live on large enterprise subscriptions that were lumpy and now has a model more in line with cloud providers and companies like Snowflake.
That transition, which appears to be largely complete, is highlighted in C3.ai's investor deck.
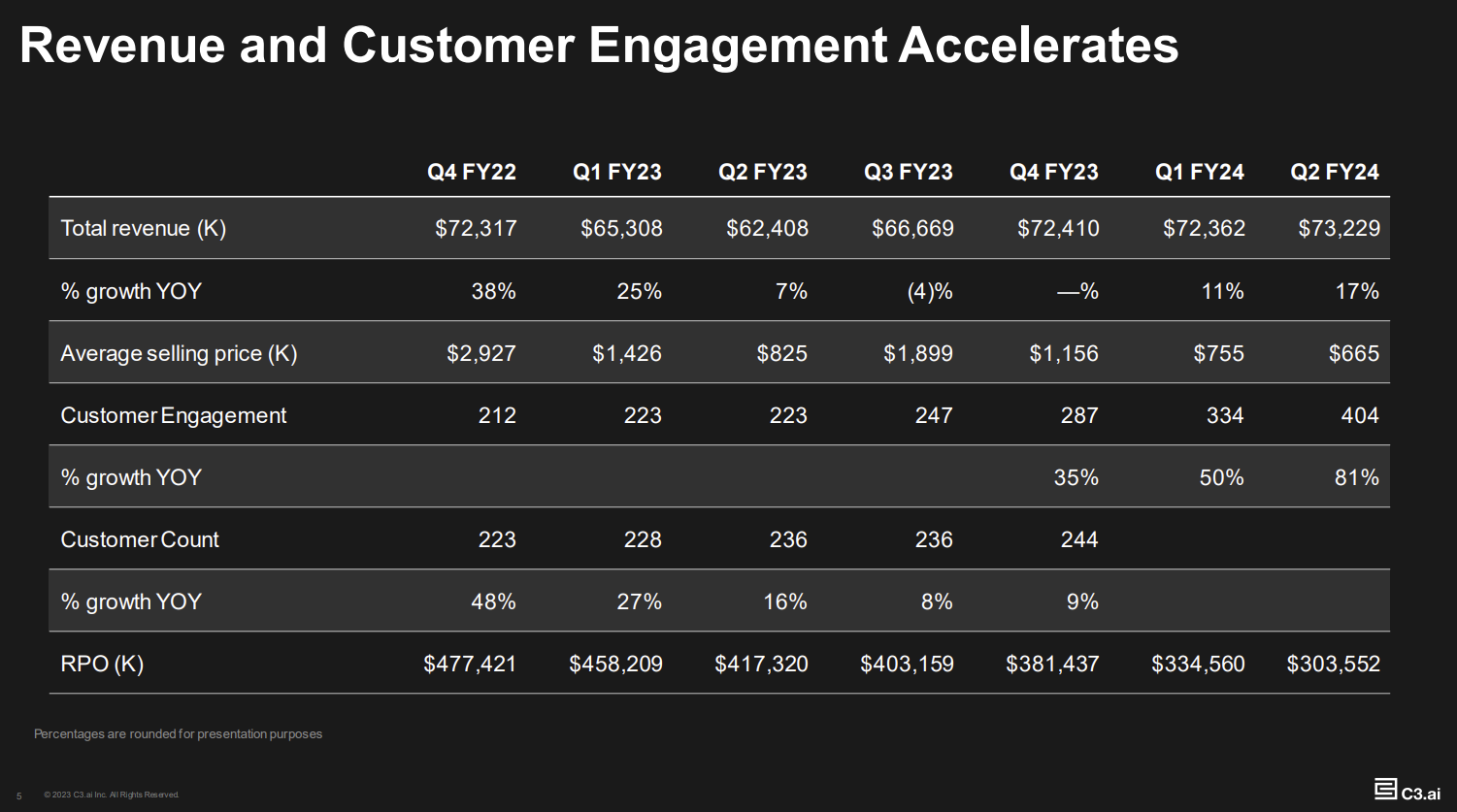
C3.ai reported second quarter revenue of $73.2 million, up 17% from a year ago. Subscription revenue was up 12% from a year ago. C3.ai reported a net loss of 59 cents a share and a non-GAAP net loss of 13 cents a share.
The company projected third quarter revenue of $74 million to $78 million, up 11% to 17% from a year ago.
In many ways, C3.ai is in the right place at the right time. Generative AI has taken off and C3.ai is a key player. I recently detailed a C3.ai project at Baker Hughes illustrating a sustainability generative AI use case (PDF).
Constellation ShortListâ„¢ Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Cloud Platforms | C3 AI launches domain-specific generative AI models, targets industries | Get ready for a parade of domain specific LLMs | C3 AI CEO Tom Siebel: Generative AI enterprise search will have wide impact
The challenge is that C3.ai's go-to-market ground game is a work in progress. C3.ai has been building out its partner network with AWS becoming a big channel as the two companies target overlapping industries. C3.ai's qualified pipeline with AWS more than doubled in the second quarter. C3.ai also has partnerships with Google Cloud, Microsoft, Booz Allen and others.
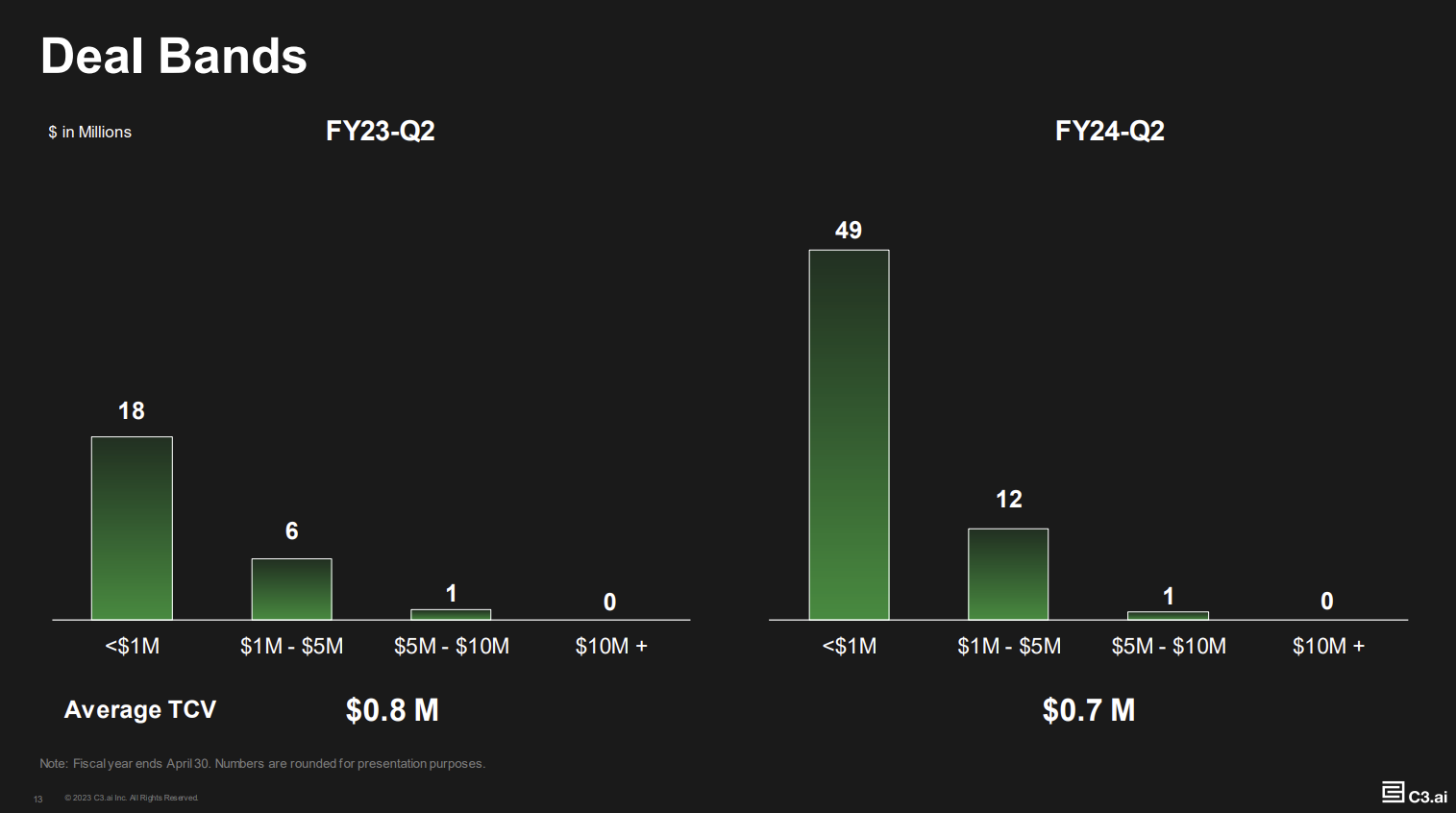
There's clearly interest in what C3.ai can offer. Bookings in the second quarter were up 100% from a year ago, new agreements were up 148% and pilots grew 177%.
Yet, these deals start small and have yet to deliver in full just yet. C3.ai is more a steady climb than a revenue rocket ship at this point. C3.ai launched with massive deals from a small number of customers--often US government agencies and large enterprises--and now is more land and expand due to generative AI.
CEO Tom Siebel said the company is converting pilots to more projects. C3.ai converted two Department of Defense logistics pilots into projects. Siebel said:
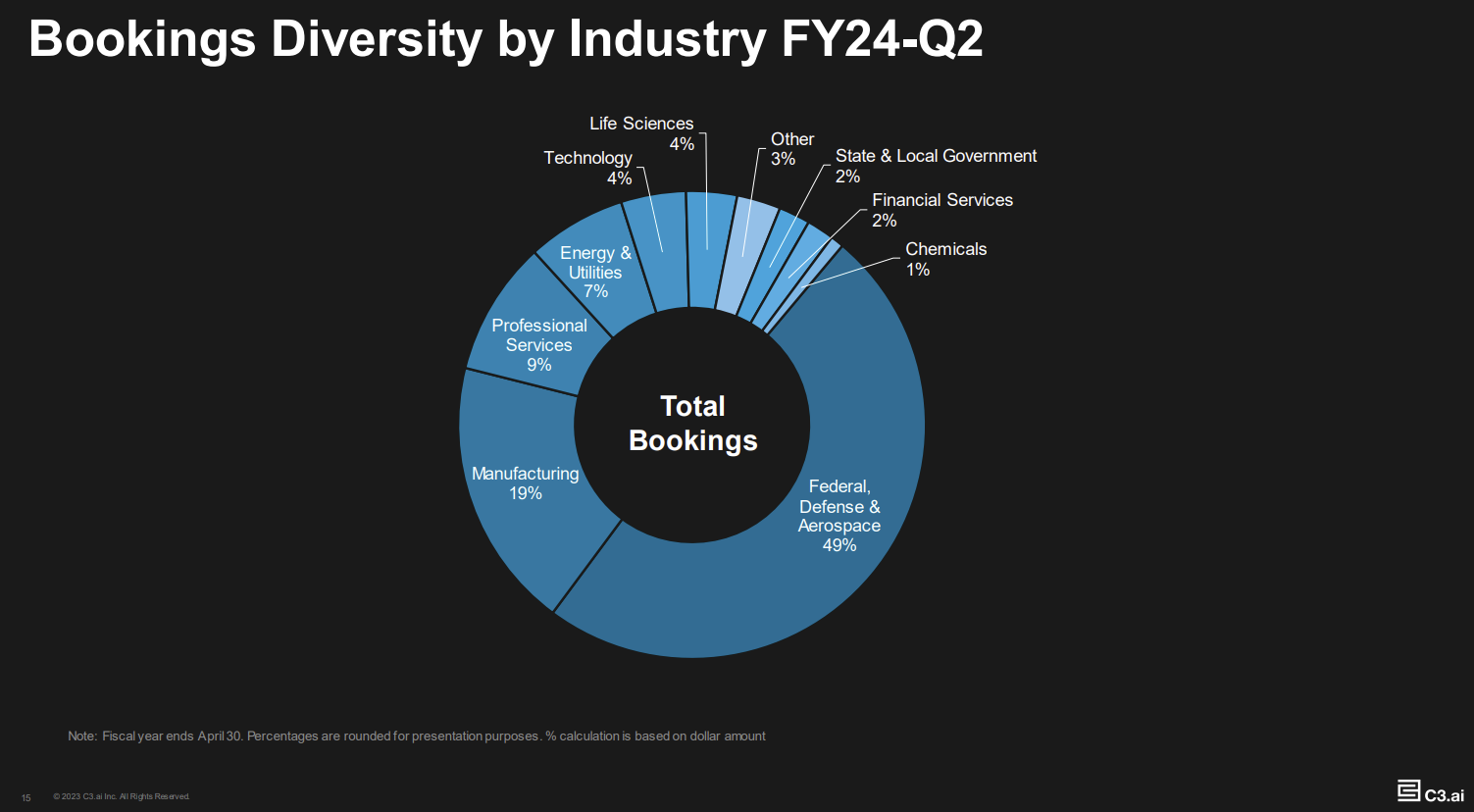
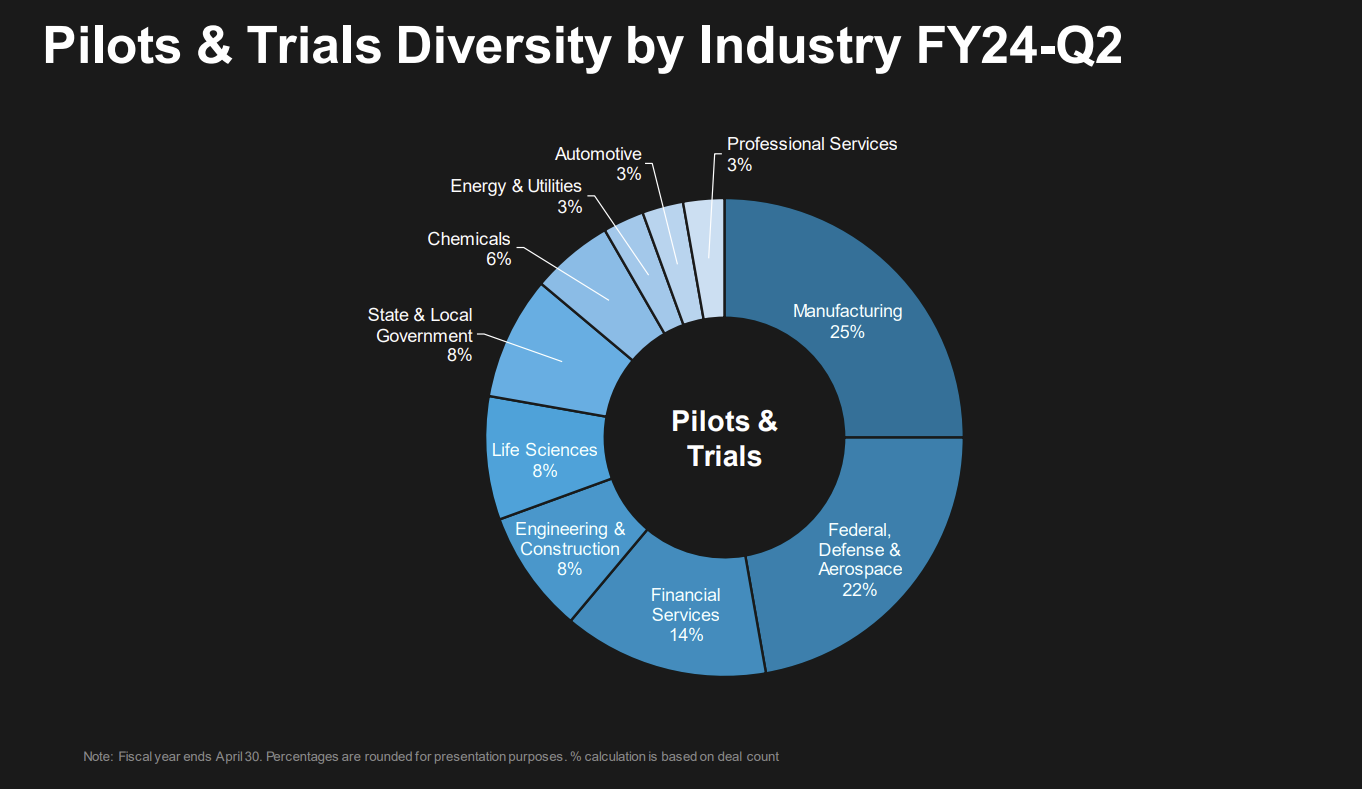
"In Q2, we closed 62 agreements, including 36 pilots and trials. Our new pilot count is up 270% from a year ago. Notably, 20 of these were generative AI pilots, a 150% increase from Q1. With the lower entry price points of our pilots, we are more easily able to land new accounts. With our pilots, we are engaging customers across a diverse set of industries in this quarter. Our pilots came from manufacturing, federal, defense, aerospace, pharmaceuticals and other industries."
Over time, C3.ai's business is going to look different. Nearly half of the company's revenue comes from federal, defense and aerospace customers. The pilots and trials underway cover many more industries.
What remains to be seen is how long it takes C3.ai to develop its revenue growth flywheel. Siebel said the sales cycle for generative AI use cases can be as fast as 24 hours with a live application in a month or two with low price points. These customers will ultimately expand their deals as C3.ai delivers value.
"The standard pilot that we have for generative AI and the enterprise is like $250,000. You can get the C3 Generative AI: AWS Marketplace Edition that’s free for 14 days," said Siebel.
Siebel did say that C3.ai is seeing interest in generative AI applications, decisions are taking longer as enterprise put governance around AI. He said:
"Virtually every company in the last 3 to 6 months has created a new AI governance function as part of its decision-making process. These AI governance functions assess and approve those AI applications that will be allowed to be installed in the enterprise. This has candidly added a step to the decision process in AI. You might have heard it here first, but you will be hearing this from every AI vendor in the next few quarters. Take it to the bank."
Overall, Siebel said more AI governance is a good development even if it lengthens the sales cycle. See: The Urgent Case for a Chief AI Officer
Siebel added that the C3 AI Platform will gain traction because it can "solve the disqualifying hobgoblins that are preventing the adoption of generative AI in government, in defense, intelligence, in the private sector."
Those issues include answers from large language models (LLMs) that aren't easily traced and can leak intellectual property and create other liabilities. Enterprises will also move toward an LLM agnostic strategy.
Siebel said:
Data to Decisions Innovation & Product-led Growth Future of Work Tech Optimization Next-Generation Customer Experience Digital Safety, Privacy & Cybersecurity ML Machine Learning LLMs Agentic AI Generative AI AI Analytics Automation business Marketing SaaS PaaS IaaS Digital Transformation Disruptive Technology Enterprise IT Enterprise Acceleration Enterprise Software Next Gen Apps IoT Blockchain CRM ERP finance Healthcare Customer Service Content Management Collaboration GenerativeAI Chief Information Officer Chief Data Officer Chief Executive Officer Chief Technology Officer Chief AI Officer Chief Analytics Officer Chief Information Security Officer Chief Product Officer"I don’t think anybody wants to hook their wagon on to any given LLM today with all the innovation that’s going on in the market and to be dependent on any LLM provider. Our solution is LLM agnostic and addresses every one of those hobgoblins that prevent the installation of generative AI in the enterprise. It took 14 years and $2 billion of software engineering for us to be ready for this."