Oracle adds generative AI features to Autonomous Database
Oracle continued to build out its generative AI tools for its Autonomous Database with conversational AI, a broad set of large language models, new analytics for knowledge graphs, spatial learning and no-code modeling.
By bringing generative AI models to its database portfolio, Oracle is looking to make models more dynamic by connecting them to real-time data. The general theme behind Autonomous Database Select AI is to enable insights in natural language without the user needing to know where and how data is stored.
Here's a breakdown of new additions to Oracle Autonomous Database:
- Select AI, which uses LLMs to generate SQL queries based on natural language conversations. Select AI enables apps to integrate private data with generative AI and supports multiple models.
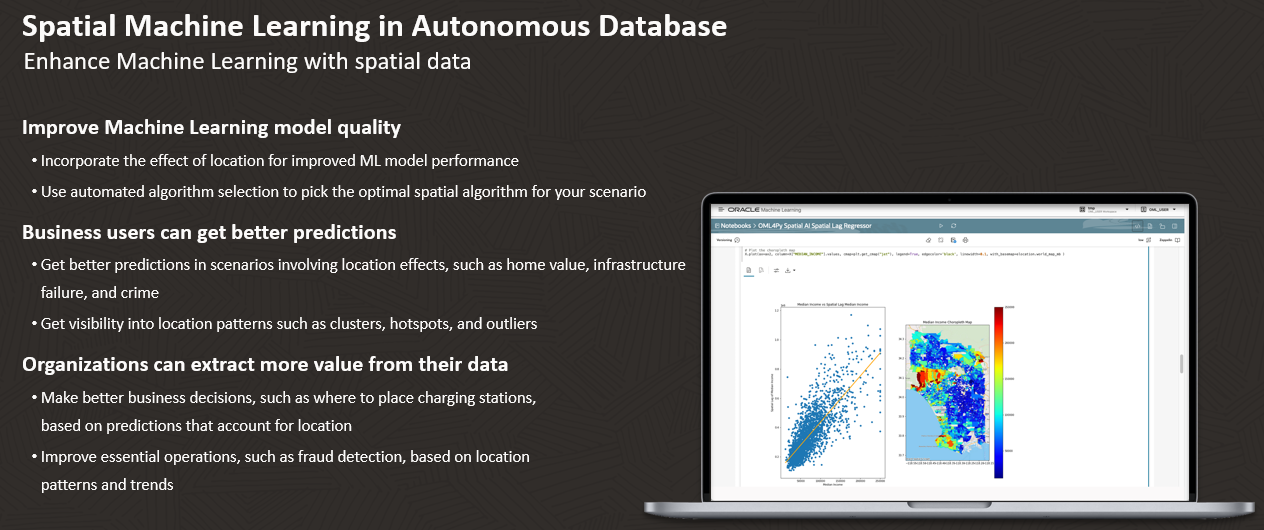
- Spatial machine learning, an addition to Oracle Machine Learning. Spatial machine learning uses location data to improve model performance and supports spatial algorithms.
- Model monitoring user interface, which is a no-code UI in Oracle Machine Learning. Model monitoring UI is designed to make it easier to monitor models and detect concept and quality drift.
- Operational graph views on knowledge graphs, a new no-code UI that facilitates graph analytics on knowledge graphs without duplicating data and examines connections.
Oracle executives said Select AI is available today in Oracle Autonomous Database and can be used in any database application. The Select AI rollout comes a few weeks after Oracle announced general availability of its Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Generative AI service and plans to integrate generative AI across its stack and applications.
Previously:

