Amazon revamps supply chain, last mile delivery, warehouses with AI models
Amazon is throwing its AI foundation model weight behind its supply chain as it optimizes routes with SCOT (Supply Chain Optimization Technology). With the move, Amazon is using its generative AI tools to highlight the returns that'll show up in its earnings results.
The company also highlighted its robotics, agentic AI and physical AI efforts.
At an event, Amazon outlined SCOT, which will touch every Amazon package in its supply chain. SCOT has an AI foundational model that powers its supply chain. Today the model processes more than 400 million items across 270 different time spans. Strategically, this supply chain, last mile delivery and robotics advance with foundational models makes a lot of sense. First it improves operations and drives real returns for Amazon. Second it's a nice showcase and first customer reference for Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- AWS Q1 revenue up 17% as Amazon tops estimates
- AWS rolls out Nova Premier on Amazon Bedrock
- AWS, Amazon court developers to take Nova models for a spin, Alexa+ goes early access
Amazon CEO Andy Jassy has made a point of highlighting how AI is helping the company's overall operations. At re:Invent 2024, Jassy talked extensively about how continous improvement in the supply chain can save a few pennies per package that add up to billions of dollars at scale. He also noted robotics and automation advances in warehouses and distribution centers.
- AWS re:Invent 2024: 7 takeaways after drinking from the firehose
- AWS CEO Garman Q&A: Model choices, competition and AI's future
- AWS re:Invent 2024: Four AWS customer vignettes with Merck, Capital One, Sprinkr, Goldman Sachs
- Amazon Bedrock vs. DIY approaches benchmarked
Constellation Research CEO R "Ray" Wang was at the Amazon event and noted:
"Amazon is showing the power of Exponential Efficiency. Just like Uber optimized ride batching, dynamic pricing, and route optimization, Amazon is using its data to drive down costs, improve customer experience, reduce delivery times and perfect orders. Digital giants in an AI age have the ability to use their data to create massive operational efficiencies and improve customer experience at machine scale."
Key points about the SCOT model include:
- SCOT is predicting what customers want before they click the buy button to reduce delivery ties by almost a day while lowering carbon emissions.
- The model predicts where they'll want orders delivered and when. SCOT also recognizes local demand patterns.
- The supply chain model ingests weather patterns and planned promotions as well as traditional data.
- Amazon said SCOT enables the company to position inventory closer to customers for fewer miles driven.
- So far, SCOT has driven a 10% improvement in long-term national forecasts and a 20% improvement regionally.
- SCOT is live in US, Canada, Mexico and Brazil. EU and other countries will be live in the near future.
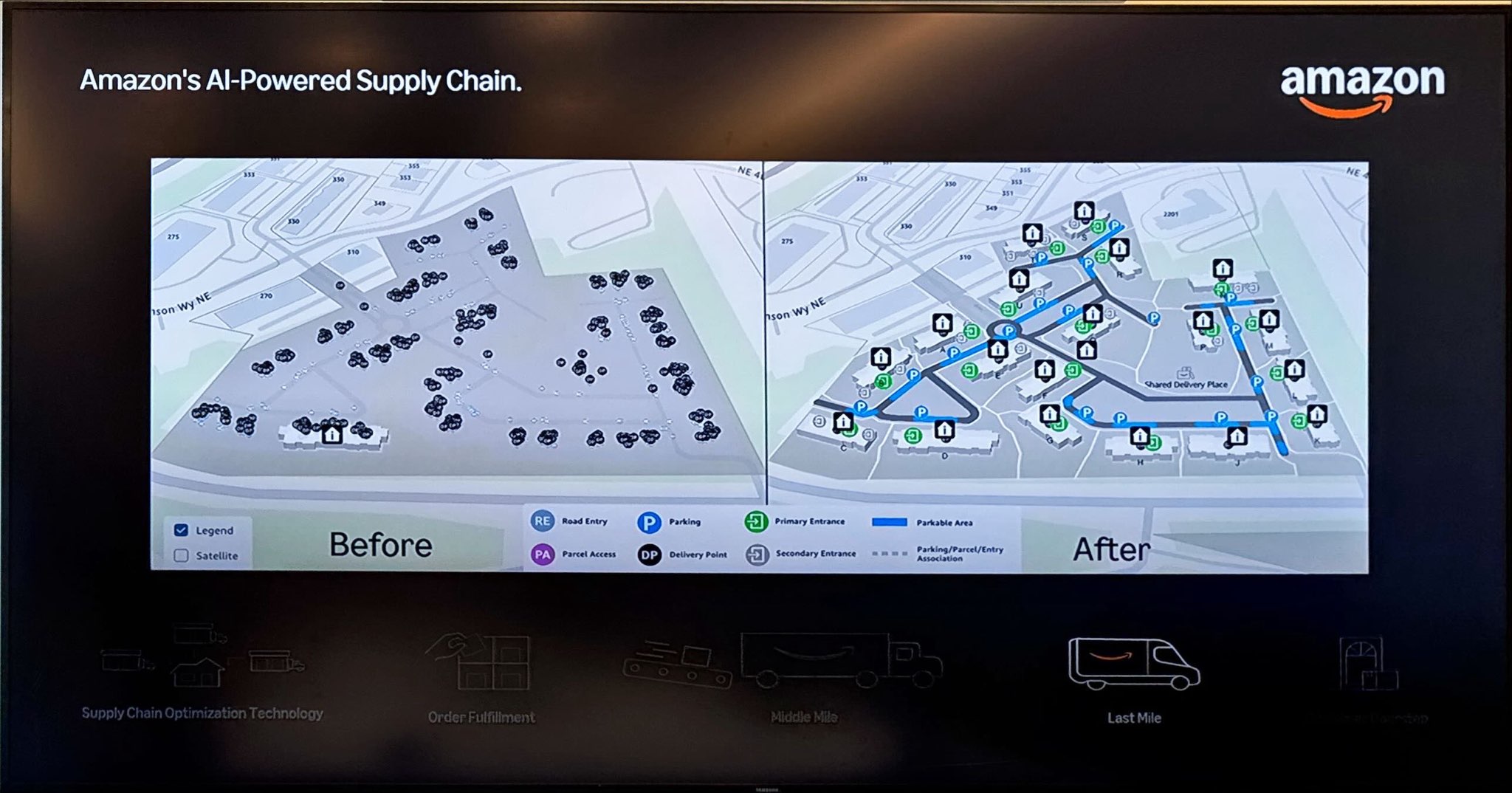
Last mile genAI meets physical AI
Amazon also launched last mile generative AI mapping that leverages satellite imagery, road networks, land parcels and building footprints along with delivery scan data and GPS data from past deliveries. All of Amazon's data is used to produce a model of where packages will be dropped off.
The company said that advances in foundational models allowed it to scale reasoning and perception across petabytes of data to fine tune without humans.
In October 2024, Amazon launched the first version of the mapping technology and was able to map more than 2.8 million apartment addresses as well as 4 million parking locations.
This data fed a more accurate geospatial model across the US that will now scale by 10x in 2025. Key items include:
AI mapping helps Amazon drivers navigate university campus and office complexes by identifying optimal parking locations.
By November, Amazon is on track to refine apartment address to building mappings for more than 11 million apartments across 700,000 campuses.
Amazon said that it will have learned more than 130 million delivery locations, 200 million parking spots and 800,000 building entrances.
Agentic AI and robotics
Amazon also outlined how Project Vulcan is combining robotics and agentic AI.
The project enables robots to hear, understand natural language and act autonomously.
According to Amazon, the goal is to create systems of robots instead of specialists so they will be more valuable in warehouse roles as assistants.
The company noted that it's moving "beyond one brain per robot†to fine-tuning a single large model that works across multiple robots, tasks and sensory inputs.

